A hospital I.V. / saline stand (also called an IV stand, IV pole, or saline stand) is a medical device used to support intravenous (IV) fluid bags or saline bottles, allowing fluids, nutrients, or medications to be administered directly into a patient’s bloodstream through an IV line.
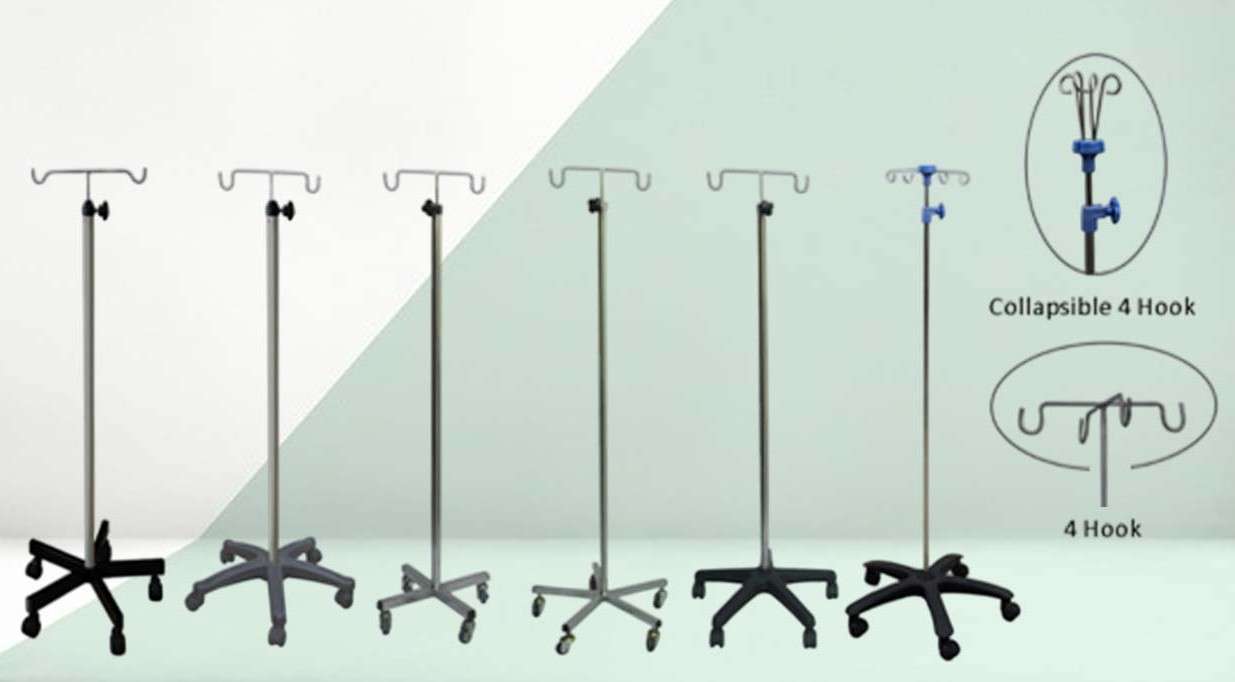
Key Components of an I.V. / Saline Stand:
Vertical Pole
- Function: Central upright structure that holds all other components together.
- Material: Usually made of stainless steel, aluminum, or chrome-plated steel to ensure durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning.
- Design: Often telescopic for height adjustment, with locking knobs to secure the desired height.
Hooks or Hangers (Top Hooks)
- Function: Used to hang IV fluid bags, saline bottles, blood bags, or medication containers.
- Quantity: Typically, 2 to 4 hooks to allow multiple infusions at once.
- Material: Often metal (stainless steel) or strong plastic, designed to withstand the weight of fluid-filled bags.
Height Adjustment Mechanism
- Function: Allows customization of the stand’s height depending on the patient’s position (e.g., lying, sitting, walking).
- Mechanism: Often uses a telescoping pole with a twist-lock, push-button, or screw-lock system.
- Range: Adjustable height typically ranges from 4 to 7 feet (120–210 cm).
Base
- Function: Provides stability to prevent tipping, especially when the stand is holding multiple bags or being moved.
- Shape: Common designs include five-legged star bases or circular bases.
- Material: Heavy-duty metal or plastic with reinforced weight to prevent toppling.
Wheels (Casters)
- Function: Enable smooth movement of the IV stand across different floor types.
- Design: Usually 4 or 5 swivel casters, with rubber coating for quiet and smooth rolling.
- Locking Mechanism: Many wheels include brakes or locks to keep the stand stationary when needed.
Accessory Holders (Optional)
- Pump Brackets: To attach infusion or syringe pumps.
- Oxygen Cylinder Holders: For respiratory support equipment.
- Trays or Baskets: To hold supplies like syringes, medication vials, or tubing.
- Clamp Attachments: For added customization or securing other devices.
Grip Handle (Optional)
- Function: Provides an easy grip for pushing or repositioning the stand.
- Placement: Usually located mid-way on the vertical pole or at the top of the base.
Uses of a Hospital I.V. / Saline Stand
Intravenous (IV) Fluid Administration
- The primary use of an IV stand is to suspend IV fluid bags or saline bottles above the patient’s level, allowing gravity or a pump to deliver fluids directly into the bloodstream.
- Fluids administered can include:
- Saline solution
- Dextrose
- Electrolyte replacements
- Plasma expanders
Medication Infusion
- Medications that require slow or continuous infusion over time—such as antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, or analgesics—are delivered using IV infusion setups supported by the stand.
- Ensures stable and safe delivery over precise durations with or without infusion pumps.
Blood Transfusion
- Used to hang blood or blood product bags during transfusions in emergency rooms, surgical theatres, or oncology wards.
- Keeps transfusion units elevated for optimal flow rate and sterility.
Parenteral Nutrition Support
- In patients who cannot eat orally or absorb nutrients via the digestive tract, Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) is delivered intravenously.
- The IV stand supports the nutrient solution bag and any secondary infusions like lipids or electrolytes.
Post-operative Care
- Post-surgery patients often require fluids, antibiotics, and pain management via IV.
- The saline stand remains at the bedside to allow continuous therapy without interrupting the patient’s rest or mobility.
Emergency & Critical Care
- In emergency rooms (ER) and intensive care units (ICU), IV stands are essential for rapid access to fluids and life-saving medications.
- Used in cases of trauma, shock, dehydration, or sepsis.
Pediatric and Neonatal Care
- Specialized IV stands are used in neonatal units to support nutritional fluids or medication delivery to infants and premature babies, ensuring precise dosing and safety.
Ambulatory Patient Mobility
- Portable IV stands allow patients to move around (e.g., walk or use the restroom) while continuing to receive IV therapy.
- This is especially helpful in recovery wards or for long-term inpatients.
Infusion Pump Support
- IV stands serve as a mounting point for electronic infusion pumps that control fluid delivery rates more precisely.
- Common in anesthesia, intensive care, and home infusion settings.
Daycare and Outpatient Procedures
- In settings such as chemotherapy clinics, dialysis centers, or outpatient infusion rooms, IV stands support regular treatments without full hospital admission.
Summary of Uses by Setting:
Setting Use
ICU & ER Emergency fluids, drugs, blood
Surgery/Post-op Fluid replacement, pain management
Oncology Chemotherapy, hydration therapy
Pediatrics/Neonatal Nutritional or therapeutic IVs
Outpatient Clinics Day treatments like IV iron, antibiotics
Rehabilitation Wards Patient mobility with continuous therapy
Benefits of Hospital I.V. / Saline Stand
Here are the detailed benefits of a Hospital I.V. / Saline Stand in medical and healthcare environments:
Efficient Fluid and Medication Delivery
- Provides a stable and elevated position for IV bags, ensuring consistent and gravity-assisted flow of fluids into the patient’s bloodstream.
- Supports the safe administration of hydration, medications, nutrients, and blood products.
Improved Patient Mobility
- Patients can move around freely (within safe limits) while still receiving IV therapy.
- Especially beneficial in recovery or rehabilitation, where mobility enhances recovery outcomes.
Versatile Usage in Different Clinical Settings
- Can be used across multiple hospital departments: emergency rooms, ICUs, operating rooms, maternity wards, pediatric units, etc.
- Also ideal for outpatient care, home infusion therapy, and ambulatory care centers.
Supports Multi-line Infusion
- Most IV stands have multiple hooks, allowing simultaneous administration of more than one fluid or medication.
- Helps in complex treatment protocols like chemotherapy, critical care, or total parenteral nutrition (TPN).
Height Adjustability for Comfort and Accuracy
- The stand’s adjustable height ensures optimal fluid flow rate and accommodates patients of different postures—sitting, lying, or walking.
- Helps nurses and doctors easily access IV ports and monitors.
Enhanced Safety and Infection Control
- The stable, hands-free hanging system reduces the risk of contamination compared to placing IV bags on surfaces.
- Easy to clean and disinfect, minimizing infection risk in clinical environments.
Accessory Support for Devices
Many IV stands support additional medical equipment, such as:
- Infusion pumps
- Syringe drivers
- Oxygen cylinders
- Instrument trays
Mobility with Safety
- Equipped with casters/wheels, IV stands allow smooth movement alongside the patient’s bed or wheelchair.
- Lockable wheels prevent unintended rolling, ensuring safety when stationary.
Cost-effective and Durable
- Made from sturdy, long-lasting materials like stainless steel or aluminum.
- Offers a high return on inves
- tment due to long service life and multipurpose use.
Improved Workflow for Healthcare Providers
- Keeps IV lines organized, reducing the chance of line tangling or confusion during multi-drug therapy.
- Frees up the hands of nurses and caregivers, improving efficiency and care delivery.
Summary of Key Benefits:
Benefit Area Description
Patient Comfort Mobility, posture adjustment, multi-drug use
Clinical Efficiency Organized, easy IV access and fluid management
Safety & Hygiene Stable, cleanable, reduces contamination risk
Equipment Integration Holds pumps, oxygen, trays for multifunction use
Cost & Durability Long-lasting, easy to maintain, reusable